Science
Astronomers Identify Massive Exomoon Candidate, Challenging Norms

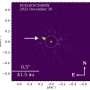
Astronomers have made a groundbreaking discovery, identifying a candidate exomoon that is believed to be significantly larger than any known moon in our solar system. This exomoon is located approximately 133 light-years from Earth and orbits a gas giant exoplanet known as HD 206893 B. The candidate has a mass estimated at around 0.4 Jupiter masses, which is more than seven times that of Neptune.
This revelation comes at a time when the astronomical community has already recorded a remarkable total of over 6,000 exoplanets since the start of the year, highlighting an ever-expanding frontier in space exploration. The discovery of this exomoon candidate could reshape our understanding of moon formation and characteristics beyond our solar system.
A Unique Method of Detection
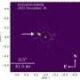
Unlike previous attempts to locate exomoons that relied on observing slight declines in star brightness during planetary transits, this discovery employed a method known as astrometry. Utilizing the Very Large Telescope in Chile and the high-precision VLTI/GRAVITY interferometer, astronomers focused on the motion of HD 206893 B over time. They were able to detect small deviations or “astrometric residuals” in the expected path of the planet, suggesting the presence of a companion body influencing its movement.
This method has allowed researchers to overcome one of the primary challenges in exomoon discovery: detecting the small transit signals produced by moons that are significantly smaller than their host planets. The gravitational perturbations observed hint at an orbiting companion with a period of approximately 0.76 years.
The host planet, HD 206893 B, is itself an extraordinary object, boasting a mass around 28 times that of Jupiter. This places it in a unique category, straddling the line between giant planets and brown dwarfs. The classification of the newly identified body remains contentious; while the discovery team designates it as a candidate exomoon, it is not classified as an equal partner to its host.
Implications for Future Research
The potential confirmation of this massive exomoon has generated excitement within the scientific community, as it challenges existing models that suggest moons are typically smaller in relation to their parent planets. If confirmed, this finding may necessitate a reevaluation of our understanding of satellite formation in the universe.
The discovery team has emphasized the provisional nature of their findings, noting that further investigation is essential to rule out the possibility that the observed residuals are the result of systematic errors or noise. This caution is warranted, especially considering the challenges faced by previous high-profile exomoon candidates, such as Kepler-1625b I, which have been difficult to verify and sometimes reclassified as artefacts.
The researchers believe that future measurements using the GRAVITY technology, along with advancements in astronomical tools, could provide the means to confirm the presence of this exomoon or others of similar magnitude. The possibility of detecting moons with masses significantly lower than that of Neptune is now within reach, paving the way for directly imaging exoplanets and brown dwarfs that have remained elusive.
As this candidate exomoon around HD 206893 B stands currently as a tantalizing prospect, ongoing scrutiny and follow-up observations will be crucial. The implications of such a discovery extend far beyond a single astronomical finding; they may open new avenues for understanding the formation and evolution of moons across the cosmos.
-

 Entertainment3 months ago
Entertainment3 months agoAnn Ming Reflects on ITV’s ‘I Fought the Law’ Drama
-

 Entertainment4 months ago
Entertainment4 months agoKate Garraway Sells £2 Million Home Amid Financial Struggles
-

 Health3 months ago
Health3 months agoKatie Price Faces New Health Concerns After Cancer Symptoms Resurface
-

 Entertainment2 weeks ago
Entertainment2 weeks agoCoronation Street Fans React as Todd Faces Heartbreaking Choice
-

 Entertainment3 months ago
Entertainment3 months agoCoronation Street’s Carl Webster Faces Trouble with New Affairs
-

 World3 weeks ago
World3 weeks agoBailey Announces Heartbreaking Split from Rebecca After Reunion
-

 Entertainment3 months ago
Entertainment3 months agoWhere is Tinder Swindler Simon Leviev? Latest Updates Revealed
-

 Entertainment4 months ago
Entertainment4 months agoMarkiplier Addresses AI Controversy During Livestream Response
-

 Science2 months ago
Science2 months agoBrian Cox Addresses Claims of Alien Probe in 3I/ATLAS Discovery
-

 Health5 months ago
Health5 months agoCarol Vorderman Reflects on Health Scare and Family Support
-

 Entertainment4 months ago
Entertainment4 months agoKim Cattrall Posts Cryptic Message After HBO’s Sequel Cancellation
-

 Entertainment3 months ago
Entertainment3 months agoOlivia Attwood Opens Up About Fallout with Former Best Friend