Science
New Levitating Sensors Set to Transform Quantum Sensing
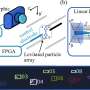
A groundbreaking development in sensor technology could significantly enhance the accuracy and efficiency of various sensing applications. Researchers from the University of California, Berkeley have created a new type of sensor that levitates dozens of glass microparticles. This innovation may not only improve autonomous vehicles and navigation systems but could also play a crucial role in the detection of dark matter.
The innovative sensors work by utilizing acoustic levitation to suspend glass particles in mid-air. This approach allows for precise measurements and the potential to detect even the faintest signals from quantum phenomena. The research team believes that harnessing these levitating sensors could lead to advancements in multiple fields, including physics, engineering, and environmental monitoring.
Potential Applications in Autonomous Technology
One of the most promising applications of this technology lies in the realm of autonomous vehicles. Enhanced sensing capabilities could lead to improved navigation and obstacle detection, making self-driving cars safer and more reliable. As the automotive industry continues to invest heavily in autonomous technology, the demand for advanced sensors that offer higher accuracy is ever-growing.
Moreover, the new sensors could facilitate real-time data collection and processing, crucial for the efficient operation of autonomous systems. By integrating these levitating sensors into vehicle designs, manufacturers could achieve a significant edge in the competitive automotive market.
Advancements in Dark Matter Detection
Beyond practical applications in transportation, the levitating sensors hold the potential to contribute to the ongoing quest to understand dark matter. This elusive substance is believed to make up approximately 27% of the universe, yet its presence has only been inferred through gravitational effects on visible matter. The ability to detect dark matter particles would provide groundbreaking insights into the fundamental structure of the universe.
According to the research team’s findings, the sensitivity of these new sensors could allow scientists to observe interactions with dark matter at unprecedented levels. This could lead to a deeper understanding of cosmic phenomena and further exploration of quantum mechanics.
In October 2023, the team published their findings in a leading physics journal, highlighting the transformative capabilities of their levitating sensors. The potential applications of this technology extend far beyond current capabilities, paving the way for future innovations in both theoretical and applied sciences.
As the research progresses, collaboration with industry partners is expected to accelerate the development and deployment of these sensors. This could lead to significant advancements in technology and science, making the previously unimaginable a reality.
The implications of this research are profound, with the potential to not only enhance everyday technologies but also to unlock the mysteries of the universe itself. As researchers continue to explore the capabilities of these levitating sensors, the future of sensing technology looks bright.
-

 Entertainment3 months ago
Entertainment3 months agoAnn Ming Reflects on ITV’s ‘I Fought the Law’ Drama
-

 Entertainment4 months ago
Entertainment4 months agoKate Garraway Sells £2 Million Home Amid Financial Struggles
-

 Health3 months ago
Health3 months agoKatie Price Faces New Health Concerns After Cancer Symptoms Resurface
-

 Entertainment3 months ago
Entertainment3 months agoCoronation Street’s Carl Webster Faces Trouble with New Affairs
-

 Entertainment2 weeks ago
Entertainment2 weeks agoCoronation Street Fans React as Todd Faces Heartbreaking Choice
-

 Entertainment3 months ago
Entertainment3 months agoWhere is Tinder Swindler Simon Leviev? Latest Updates Revealed
-

 World2 weeks ago
World2 weeks agoBailey Announces Heartbreaking Split from Rebecca After Reunion
-

 Entertainment4 months ago
Entertainment4 months agoMarkiplier Addresses AI Controversy During Livestream Response
-

 Science1 month ago
Science1 month agoBrian Cox Addresses Claims of Alien Probe in 3I/ATLAS Discovery
-

 Health5 months ago
Health5 months agoCarol Vorderman Reflects on Health Scare and Family Support
-

 Entertainment4 months ago
Entertainment4 months agoKim Cattrall Posts Cryptic Message After HBO’s Sequel Cancellation
-

 Entertainment3 months ago
Entertainment3 months agoOlivia Attwood Opens Up About Fallout with Former Best Friend