Science
Astronomers Discover Unique Jet in Interstellar Object 3I/ATLAS
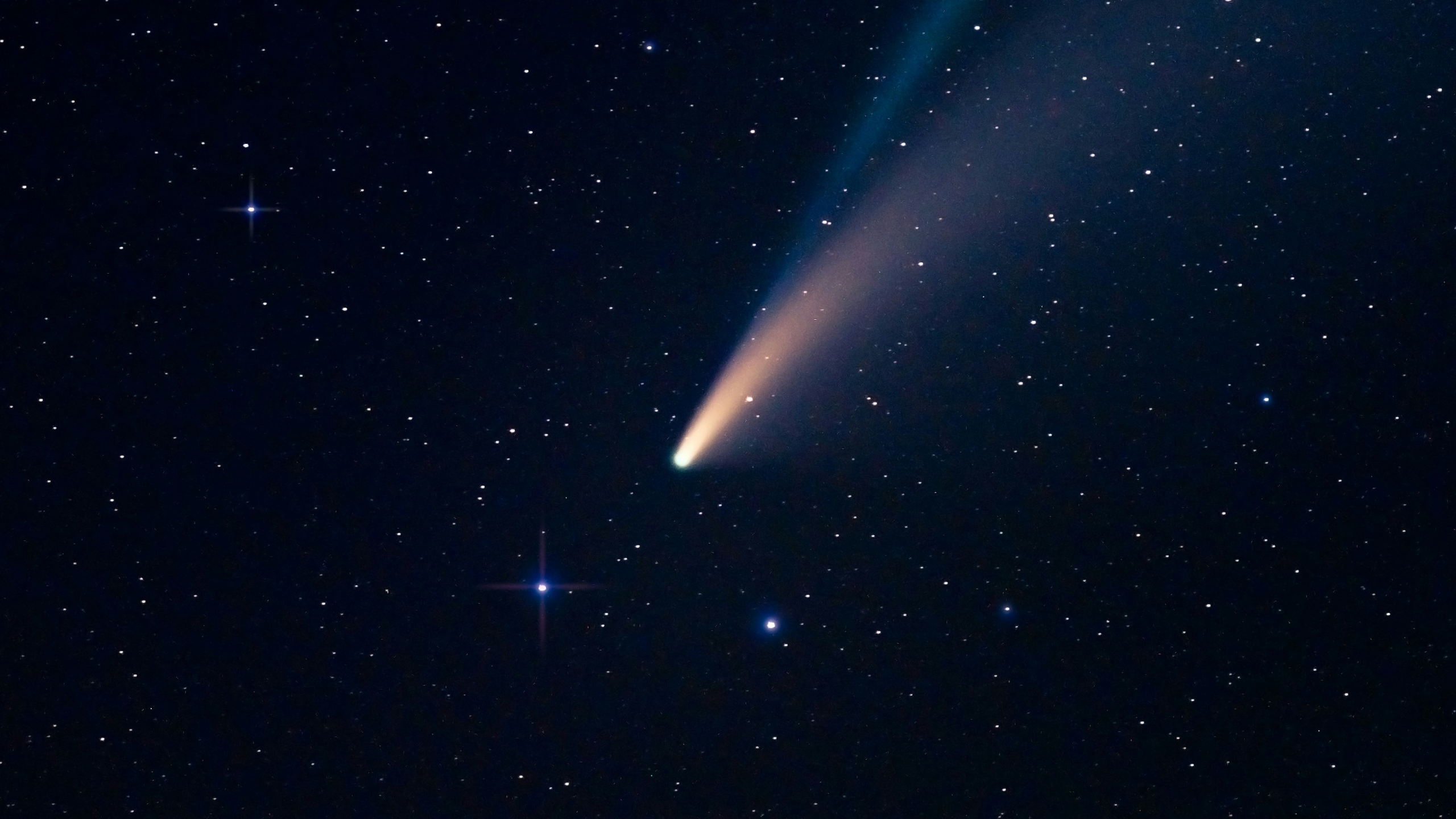

The interstellar object known as 3I/ATLAS has captured the attention of astronomers worldwide following its unexpected discovery by the ATLAS telescope in Chile in July 2025. Estimated to measure between 20 and 40 kilometres, this celestial body is on a hyperbolic trajectory, travelling at speeds exceeding 50 kilometres per second, which confirms its origin from outside our solar system. This marks the third confirmed interstellar visitor, following the notable 1I/’Oumuamua in 2017 and 2I/Borisov in 2019.
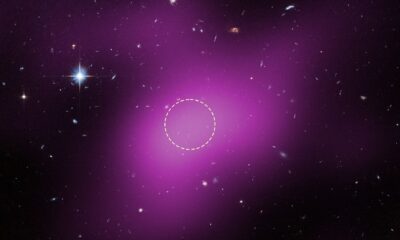
What sets 3I/ATLAS apart from its predecessors is the presence of a peculiar jet that points directly towards the Sun. In typical comets, jets are formed by solar radiation and solar wind, causing tails to extend away from the Sun. In contrast, observations of 3I/ATLAS indicate a small jet directed towards the Sun, with its nucleus located approximately 6,000 kilometres away.
Scientific Debate Surrounds Jet Phenomenon
Harvard astrophysicist Avi Loeb has raised significant questions regarding the behaviour of this jet. He argues that the observed characteristics are inconsistent with standard cometary physics. In his analysis, Loeb noted that if 3I/ATLAS were a conventional comet, the antitail jet should not extend beyond 5,000 kilometres. This anomaly has sparked controversy within the scientific community, as researchers consider whether the jet could be the result of unusual outgassing patterns due to the object’s unique composition.
Some scientists propose that the orientation and intensity of the jet may reveal new processes in interstellar comets that have yet to be documented. Loeb has identified eight anomalies associated with 3I/ATLAS, including its trajectory, spectral signatures, and the sunward jet itself. While he presents intriguing possibilities, many mainstream astronomers caution against jumping to conclusions, stressing the need for additional data before forming definitive interpretations.
The jet was captured in images taken by the Two-Meter Twin Telescope in the Canary Islands in August 2025. A synthesis of 159 images revealed a striking purple jet extending towards the Sun, with a yellow line indicating where a conventional comet tail would typically appear. Further analysis from the ESA XMM-Newton spacecraft indicated the emission of low-energy X-rays, resulting from gases emitted by 3I/ATLAS interacting with the solar wind. These findings reinforce the notion that the object is actively outgassing, but the mechanics remain poorly understood under current models.
Implications for Understanding Interstellar Objects
The anomalies presented by 3I/ATLAS highlight the challenges faced by researchers studying interstellar objects. Each encounter with such celestial visitors provides a rare opportunity to test existing hypotheses about planetary system formation and the behaviour of bodies in the outer reaches of space. The presence of a sunward jet raises significant questions about the object’s composition and internal structure.
If the jet is propelled by materials atypical of solar system comets, it could offer insights into the diversity of interstellar matter. Alternatively, if the jet’s direction is influenced by rotational forces or other phenomena, it may enhance our understanding of cometary physics.
While there has been speculation regarding a non-natural origin for the jet, the prevailing scientific view remains skeptical. Astronomers emphasize that unusual behaviour does not necessarily imply extraordinary explanations. Instead, the focus is on gathering more data, especially as 3I/ATLAS approaches perihelion and moves further from the solar system.
Loeb himself reiterates that as a comet, the jet and antitail should not produce streaming gas beyond 5,000 kilometres. This statement underscores the necessity of comparing traditional models with new evidence, rather than hastily reaching conclusions.
The case of 3I/ATLAS exemplifies how interstellar visitors can challenge established astronomical paradigms. The sunward jet presents an apparent oddity that could either clarify its nature as a uniquely behaving comet or represent a broader category of interstellar objects that remain largely unexplored. As the scientific community continues to observe and analyze this intriguing interstellar visitor, each encounter represents a valuable opportunity to expand our understanding of the universe.
-

 World1 month ago
World1 month agoCoronation Street’s Shocking Murder Twist Reveals Family Secrets
-

 Entertainment1 month ago
Entertainment1 month agoAndrew Pierce Confirms Departure from ITV’s Good Morning Britain
-

 Entertainment6 months ago
Entertainment6 months agoKate Garraway Sells £2 Million Home Amid Financial Struggles
-

 Health5 months ago
Health5 months agoKatie Price Faces New Health Concerns After Cancer Symptoms Resurface
-

 Entertainment5 months ago
Entertainment5 months agoAnn Ming Reflects on ITV’s ‘I Fought the Law’ Drama
-

 World2 months ago
World2 months agoBailey Announces Heartbreaking Split from Rebecca After Reunion
-

 Entertainment1 month ago
Entertainment1 month agoDavid Jason and Nicholas Lyndhurst Eye Reunion for Only Fools Anniversary
-

 Entertainment2 months ago
Entertainment2 months agoCoronation Street Fans React as Todd Faces Heartbreaking Choice
-

 Entertainment2 months ago
Entertainment2 months agoBradley Walsh Sparks Strictly Come Dancing Hosting Speculation
-

 Entertainment1 month ago
Entertainment1 month agoTwo Stars Evicted from I’m A Celebrity Just Days Before Finale
-

 Entertainment5 months ago
Entertainment5 months agoCoronation Street’s Carl Webster Faces Trouble with New Affairs
-

 World1 month ago
World1 month agoKevin Sinfield Exceeds Fundraising Goal Ahead of Final Marathons