Science
Study Reveals CDT1 Overexpression Causes DNA Damage Linked to Cancer
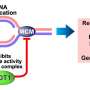
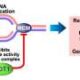
Research from a team of scientists has uncovered that the overexpression of Cdc10-dependent transcript 1 (CDT1) significantly suppresses DNA replication, leading to DNA damage that may contribute to cancer development. This discovery sheds light on the potential role of CDT1 in genetic mutations, an area that has remained ambiguous despite prior investigations linking its overexpression to cancerous changes in cells.
The study highlights how elevated levels of CDT1 disrupt normal DNA replication processes. This disruption is critical as DNA replication is essential for cell division and the maintenance of genetic integrity. When CDT1 levels rise, the likelihood of DNA damage increases, which can result in mutations. Such mutations are a known precursor to various forms of cancer, making this finding particularly significant for cancer research.
Unraveling the Mechanisms Behind CDT1
Although earlier studies indicated a connection between CDT1 overexpression and tumorigenesis, the exact mechanisms involved had not been clearly defined. This new research provides deeper insights, suggesting that the pathway through which CDT1 affects DNA replication is crucial for understanding its role in cancer biology. Understanding these mechanisms could pave the way for targeted therapies that address the effects of CDT1 on DNA integrity.
The team conducted comprehensive experiments to analyze the impacts of CDT1 on DNA replication. They discovered that the overexpressed protein interferes with the normal initiation of DNA replication, leading to stalling and subsequent DNA damage. This process is particularly concerning in the context of rapidly dividing cells, such as those found in tumors.
The implications of this research extend beyond basic science, potentially affecting clinical approaches to cancer treatment. By targeting CDT1 pathways, it may be possible to develop strategies that mitigate the adverse effects of its overexpression, thereby reducing the risk of cancer progression.
As the scientific community continues to explore the complexities of cancer biology, findings like these highlight the importance of understanding regulatory proteins such as CDT1. With ongoing research, there is the potential to unlock new avenues for prevention and treatment, ultimately improving patient outcomes in cancer care.
-

 Entertainment3 months ago
Entertainment3 months agoAnn Ming Reflects on ITV’s ‘I Fought the Law’ Drama
-

 Entertainment4 months ago
Entertainment4 months agoKate Garraway Sells £2 Million Home Amid Financial Struggles
-

 Health3 months ago
Health3 months agoKatie Price Faces New Health Concerns After Cancer Symptoms Resurface
-

 Entertainment3 weeks ago
Entertainment3 weeks agoCoronation Street Fans React as Todd Faces Heartbreaking Choice
-

 Entertainment3 months ago
Entertainment3 months agoCoronation Street’s Carl Webster Faces Trouble with New Affairs
-

 World3 days ago
World3 days agoKevin Sinfield Exceeds Fundraising Goal Ahead of Final Marathons
-

 Entertainment3 days ago
Entertainment3 days agoTwo Stars Evicted from I’m A Celebrity Just Days Before Finale
-

 World3 weeks ago
World3 weeks agoBailey Announces Heartbreaking Split from Rebecca After Reunion
-

 Entertainment3 months ago
Entertainment3 months agoWhere is Tinder Swindler Simon Leviev? Latest Updates Revealed
-

 Entertainment4 months ago
Entertainment4 months agoMarkiplier Addresses AI Controversy During Livestream Response
-

 Science2 months ago
Science2 months agoBrian Cox Addresses Claims of Alien Probe in 3I/ATLAS Discovery
-

 Health5 months ago
Health5 months agoCarol Vorderman Reflects on Health Scare and Family Support