Science
Researchers Transform Tumor-Educated Extracellular Vesicles for Drug Delivery
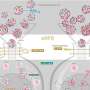
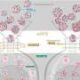
Researchers at National Taiwan University have made a significant breakthrough in cancer treatment by developing a modular platform that reprograms tumor-derived extracellular vesicles (EVs). This innovative approach transforms these vesicles from being oncogenic messengers into safe, customizable drug delivery vehicles through precise molecular editing.
The study, recently published in a leading scientific journal, highlights the potential of EVs in cancer therapy. Traditionally, tumor-derived EVs have been associated with promoting cancer progression and metastasis. Now, with this new technology, researchers aim to repurpose these vesicles for therapeutic use, potentially enhancing the efficacy of cancer treatments while minimizing side effects.
The modular platform allows for the targeted modification of the EVs, enabling researchers to control their properties and functions. By editing their molecular composition, scientists can customize these vesicles to carry specific drugs directly to tumor sites. This targeted delivery system could significantly improve treatment outcomes for cancer patients.
Advancing Cancer Treatment
The implications of this research extend beyond just cancer therapy. The ability to engineer EVs for drug delivery could revolutionize how various diseases are treated. The versatility of the platform means it can potentially be adapted for use in delivering other types of therapeutics, including RNA-based drugs and proteins.
Researchers believe that this advancement represents a pivotal moment in the field of cancer treatment. Dr. Yung-Chih Chen, the lead researcher, emphasized the importance of this technology in overcoming the limitations of traditional drug delivery methods. “Our work demonstrates that we can harness the body’s own mechanisms to create effective, targeted therapies,” Dr. Chen stated.
The study also underscores the significance of interdisciplinary collaboration in scientific research. The team at National Taiwan University combined expertise from molecular biology, materials science, and medical research to achieve these results. Their collaborative efforts highlight the importance of diverse scientific perspectives in tackling complex health challenges.
Future Directions and Potential Impact
Moving forward, the research team plans to conduct further studies to evaluate the safety and efficacy of these engineered EVs in clinical settings. The goal is to initiate clinical trials within the next few years, with hopes of bringing this innovative treatment option to patients.
The potential impact of this research on global health could be substantial. With cancer remaining one of the leading causes of mortality worldwide, advancements in targeted therapies are crucial. The ability to deliver drugs directly to tumors could not only improve patient outcomes but also reduce the overall burden of cancer treatment on healthcare systems.
This breakthrough at National Taiwan University represents a promising step towards a new era in cancer therapy, where engineered extracellular vesicles could play a crucial role in the fight against cancer. As researchers continue to refine this technology, the hope is that it will lead to more effective and accessible treatment options for patients around the globe.
-

 World1 month ago
World1 month agoCoronation Street’s Shocking Murder Twist Reveals Family Secrets
-

 Entertainment1 month ago
Entertainment1 month agoAndrew Pierce Confirms Departure from ITV’s Good Morning Britain
-

 Entertainment6 months ago
Entertainment6 months agoKate Garraway Sells £2 Million Home Amid Financial Struggles
-

 Health5 months ago
Health5 months agoKatie Price Faces New Health Concerns After Cancer Symptoms Resurface
-

 Entertainment5 months ago
Entertainment5 months agoAnn Ming Reflects on ITV’s ‘I Fought the Law’ Drama
-

 World2 months ago
World2 months agoBailey Announces Heartbreaking Split from Rebecca After Reunion
-

 Entertainment1 month ago
Entertainment1 month agoDavid Jason and Nicholas Lyndhurst Eye Reunion for Only Fools Anniversary
-

 Entertainment2 months ago
Entertainment2 months agoCoronation Street Fans React as Todd Faces Heartbreaking Choice
-

 Entertainment2 months ago
Entertainment2 months agoBradley Walsh Sparks Strictly Come Dancing Hosting Speculation
-

 Entertainment1 month ago
Entertainment1 month agoTwo Stars Evicted from I’m A Celebrity Just Days Before Finale
-

 Entertainment5 months ago
Entertainment5 months agoCoronation Street’s Carl Webster Faces Trouble with New Affairs
-

 World2 months ago
World2 months agoKevin Sinfield Exceeds Fundraising Goal Ahead of Final Marathons