Health
Research Links Dog Kisses to Improved Gut Health
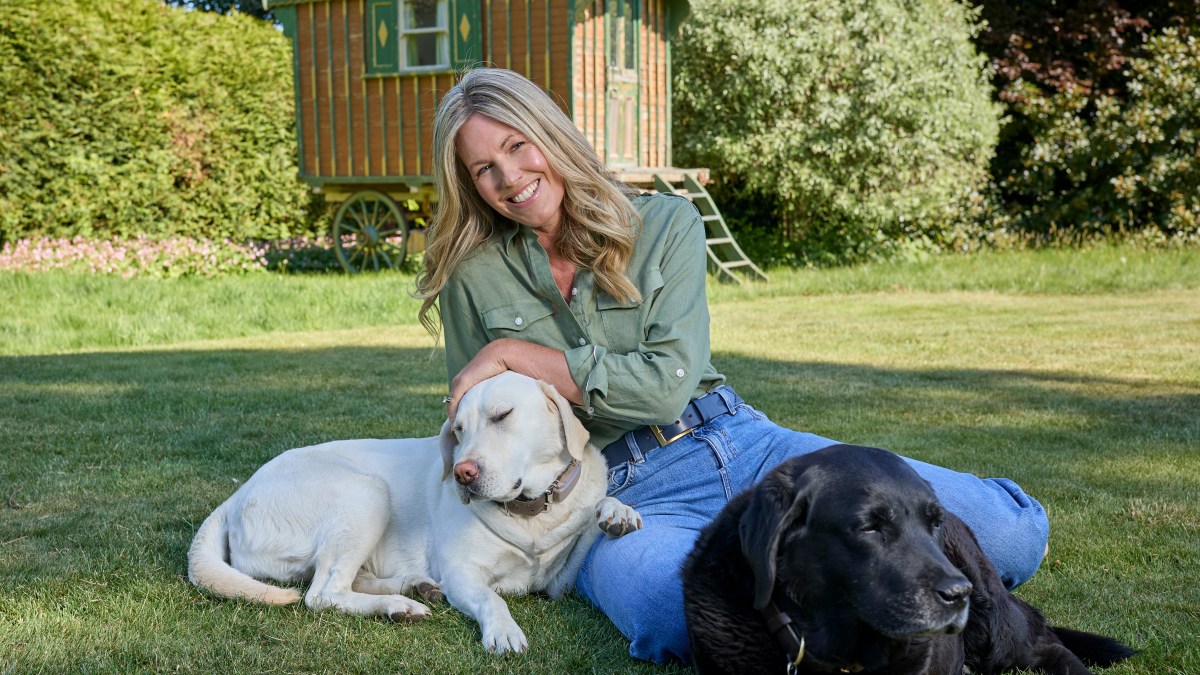

Recent research from the University of Arizona indicates that allowing dogs to lick their owners may positively influence gut health. The study suggests that exposure to canine bacteria can enhance the diversity of the gut microbiome, which plays a crucial role in overall health.
Pet ownership has long been associated with various health benefits, but this research adds a new dimension to the conversation. While petting and cuddling dogs are common practices among owners, the act of kissing or allowing dogs to lick their owners is often viewed with hesitation due to hygiene concerns. However, the findings challenge this perspective.
Understanding the Benefits of Canine Interaction
The gut microbiome consists of trillions of microorganisms that aid in digestion and influence immune function. Research shows that a diverse microbiome can lead to better health outcomes, including reduced risk of diseases such as obesity and diabetes. According to the study’s lead author, Dr. Julie M. McCafferty, “The introduction of beneficial bacteria from dogs can be a key factor in enhancing the gut microbiota of their owners.”
The study analyzed samples from both dog and human saliva, focusing on the transmission of specific bacterial strains. Findings revealed that the bacteria found in dog saliva can contribute to a more robust gut microbiome in humans. This may explain why dog owners often report feeling healthier and happier.
Implications for Pet Owners
The implications of this research are significant for pet owners and healthcare professionals alike. It suggests that allowing pets to interact closely with their owners might not only foster emotional bonds but also provide tangible health benefits. As well as enhancing gut health, the companionship of dogs has been linked to lower levels of stress and anxiety.
While the study presents compelling evidence, experts advise caution regarding hygiene practices. Regular veterinary check-ups and maintaining a clean environment for pets remain essential. The benefits highlighted by the research do not negate the importance of hygiene, particularly in households with young children or immunocompromised individuals.
As pet ownership continues to rise globally, understanding the health implications of such relationships becomes increasingly important. The findings from this study encourage dog owners to embrace their furry companions, suggesting that the benefits extend beyond emotional support to include physical health improvements.
In summary, the University of Arizona’s research presents a novel perspective on the interaction between humans and their dogs. The potential health advantages of allowing canine companionship to influence gut health open new avenues for exploring the impact of pets on human well-being.
-

 Entertainment3 months ago
Entertainment3 months agoAnn Ming Reflects on ITV’s ‘I Fought the Law’ Drama
-

 Entertainment4 months ago
Entertainment4 months agoKate Garraway Sells £2 Million Home Amid Financial Struggles
-

 Health3 months ago
Health3 months agoKatie Price Faces New Health Concerns After Cancer Symptoms Resurface
-

 Entertainment2 weeks ago
Entertainment2 weeks agoCoronation Street Fans React as Todd Faces Heartbreaking Choice
-

 Entertainment3 months ago
Entertainment3 months agoCoronation Street’s Carl Webster Faces Trouble with New Affairs
-

 World3 weeks ago
World3 weeks agoBailey Announces Heartbreaking Split from Rebecca After Reunion
-

 Entertainment3 months ago
Entertainment3 months agoWhere is Tinder Swindler Simon Leviev? Latest Updates Revealed
-

 Entertainment4 months ago
Entertainment4 months agoMarkiplier Addresses AI Controversy During Livestream Response
-

 Science2 months ago
Science2 months agoBrian Cox Addresses Claims of Alien Probe in 3I/ATLAS Discovery
-

 Health5 months ago
Health5 months agoCarol Vorderman Reflects on Health Scare and Family Support
-

 Entertainment4 months ago
Entertainment4 months agoKim Cattrall Posts Cryptic Message After HBO’s Sequel Cancellation
-

 Entertainment3 months ago
Entertainment3 months agoOlivia Attwood Opens Up About Fallout with Former Best Friend