Science
New Millipede Compounds Discovered to Influence Ant Brain Activity

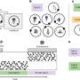
Chemist Emily Mevers and her research team at Virginia Tech have uncovered a new series of compounds from millipede secretions that can influence specific neuroreceptors in ant brains. Published on July 25, 2025, in the Journal of the American Chemical Society, this discovery highlights the potential of these compounds for future medical applications, particularly in pain management.
Discovery of Andrognathanols and Andrognathines
The newly identified compounds, named andrognathanols and andrognathines, were derived from the millipede species Andrognathus corticarius, which resides in the Stadium Woods area of the Virginia Tech campus. This research is part of Mevers’ broader effort to utilize the chemistry of underexplored ecological niches for drug discovery.
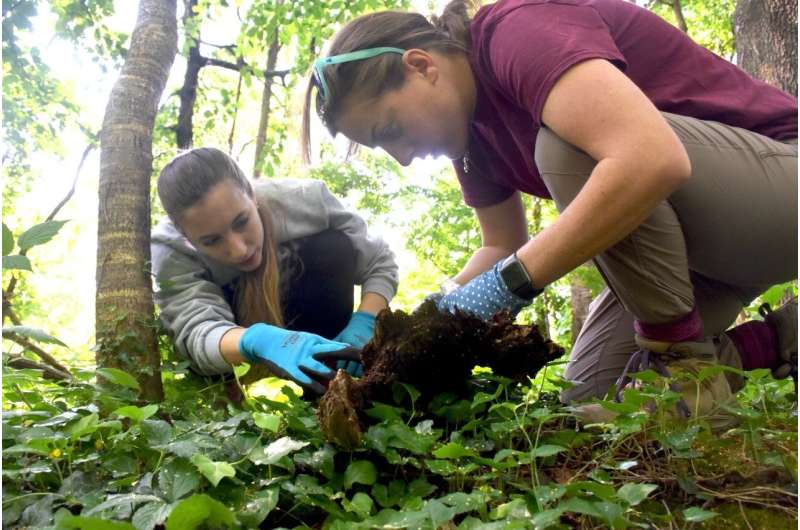
To isolate these compounds, Mevers and her team collected millipedes from leaf litter and fallen branches, employing advanced analytical techniques to analyze the chemical makeup of the millipedes’ defensive secretions. These secretions not only deter predators but also serve a communicative function among the millipedes themselves.
Significance and Future Drug Development
Despite their widespread presence, many aspects of millipedes remain poorly understood, including their habitats and behaviors. Mevers is collaborating with entomologist Paul Marek to address these knowledge gaps and explore the potential medical uses of their findings. Previously, the team had studied another millipede species, Ishcnocybe plicata, discovering that similar alkaloids interact selectively with the Sigma-1 neuroreceptor, suggesting a promising avenue for pharmacological research.
The newly discovered alkaloids are released from the Hokie millipede when disturbed, causing disorientation in ants, which are considered natural predators. Some compounds from this new class also exhibit similar interactions with the Sigma-1 neuroreceptor, indicating their potential for treating pain and neurological disorders.
With the identification of these complex compounds, the next phase involves synthesizing them in larger quantities for further evaluation. “These compounds are quite complex, so they’re going to take some time to synthesize in the lab,” Mevers stated. Once sufficient quantities are produced, the research team will investigate their properties and possible biomedical applications.
The ongoing research into millipede secretions not only contributes to our understanding of these creatures but also opens new pathways for innovative pain relief treatments and other medical interventions.
-

 Entertainment3 months ago
Entertainment3 months agoAnn Ming Reflects on ITV’s ‘I Fought the Law’ Drama
-

 Entertainment4 months ago
Entertainment4 months agoKate Garraway Sells £2 Million Home Amid Financial Struggles
-

 Health3 months ago
Health3 months agoKatie Price Faces New Health Concerns After Cancer Symptoms Resurface
-

 Entertainment3 months ago
Entertainment3 months agoCoronation Street’s Carl Webster Faces Trouble with New Affairs
-

 Entertainment3 months ago
Entertainment3 months agoWhere is Tinder Swindler Simon Leviev? Latest Updates Revealed
-

 Entertainment4 months ago
Entertainment4 months agoMarkiplier Addresses AI Controversy During Livestream Response
-

 World2 weeks ago
World2 weeks agoBailey Announces Heartbreaking Split from Rebecca After Reunion
-

 Science1 month ago
Science1 month agoBrian Cox Addresses Claims of Alien Probe in 3I/ATLAS Discovery
-

 Entertainment2 weeks ago
Entertainment2 weeks agoCoronation Street Fans React as Todd Faces Heartbreaking Choice
-

 Health4 months ago
Health4 months agoCarol Vorderman Reflects on Health Scare and Family Support
-

 Entertainment4 months ago
Entertainment4 months agoKim Cattrall Posts Cryptic Message After HBO’s Sequel Cancellation
-

 Entertainment3 months ago
Entertainment3 months agoOlivia Attwood Opens Up About Fallout with Former Best Friend