Science
Ancient Chinese Skull Discovery Challenges Human Evolution Timeline
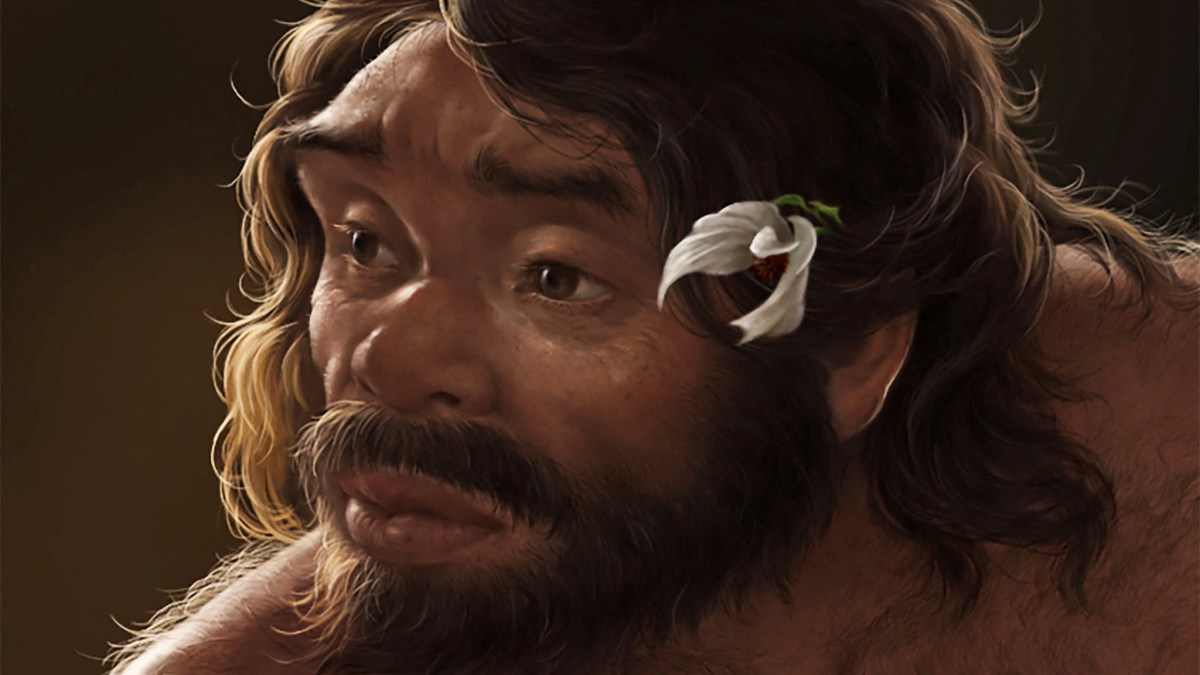

A recently unearthed skull, known as Yunxian 2, is prompting a reevaluation of the timeline of human evolution. Discovered in China, this skull is believed to be approximately one million years old. Findings suggest that Homo sapiens may have appeared in Asia up to 400,000 years earlier than previously thought, challenging the long-held belief that modern humans first evolved in Africa.
The significance of the Yunxian 2 skull was highlighted in a research paper published in March 2024 by a team from Academia Sinica and the University of Chinese Academy of Sciences. The researchers assert that this discovery provides crucial evidence that could reshape our understanding of human ancestry and migration patterns.
Implications for Human Evolution Theory
Traditionally, the prevailing theory has positioned Africa as the cradle of humanity, where anatomically modern humans emerged around 200,000 years ago. However, the Yunxian 2 skull raises questions about this narrative. The research team discovered that certain anatomical features of the skull align more closely with those of modern humans than with other earlier hominins.
Dr. Li Yi, one of the lead researchers, noted, “The anatomical characteristics of the Yunxian 2 skull suggest that the evolution of Homo sapiens may have occurred in multiple locations rather than being confined to Africa.” This perspective aligns with a growing body of evidence indicating that human evolution was a complex process influenced by various environmental factors.
The Yunxian 2 discovery also adds to a series of significant archaeological finds in East Asia. Prior discoveries, such as fossils from the Dmanisi site in Georgia and the Javanese fossils in Indonesia, have already hinted at the possibility of earlier migrations out of Africa.
Future Research Directions
As the implications of the Yunxian 2 skull continue to unfold, researchers are calling for further studies to analyze the genetic material associated with early human fossils in Asia. Understanding the relationships between these ancient remains may provide deeper insights into the evolutionary history of our species.
The interdisciplinary nature of this research, involving both archaeology and genetics, is essential for piecing together the puzzle of human evolution. It is anticipated that future findings will either support or further challenge the existing theories regarding the origins of Homo sapiens.
In conclusion, the discovery of the Yunxian 2 skull marks a potential turning point in our understanding of human evolution. As researchers delve deeper into this ancient relic, the narrative of how and when modern humans emerged may be rewritten, highlighting the complex journey of our ancestors across the globe.
-

 Entertainment3 months ago
Entertainment3 months agoAnn Ming Reflects on ITV’s ‘I Fought the Law’ Drama
-

 Entertainment4 months ago
Entertainment4 months agoKate Garraway Sells £2 Million Home Amid Financial Struggles
-

 Health3 months ago
Health3 months agoKatie Price Faces New Health Concerns After Cancer Symptoms Resurface
-

 Entertainment3 months ago
Entertainment3 months agoCoronation Street’s Carl Webster Faces Trouble with New Affairs
-

 Entertainment3 months ago
Entertainment3 months agoWhere is Tinder Swindler Simon Leviev? Latest Updates Revealed
-

 Entertainment4 months ago
Entertainment4 months agoMarkiplier Addresses AI Controversy During Livestream Response
-

 Science1 month ago
Science1 month agoBrian Cox Addresses Claims of Alien Probe in 3I/ATLAS Discovery
-

 Health4 months ago
Health4 months agoCarol Vorderman Reflects on Health Scare and Family Support
-

 World2 weeks ago
World2 weeks agoBailey Announces Heartbreaking Split from Rebecca After Reunion
-

 Entertainment4 months ago
Entertainment4 months agoKim Cattrall Posts Cryptic Message After HBO’s Sequel Cancellation
-

 Entertainment3 months ago
Entertainment3 months agoOlivia Attwood Opens Up About Fallout with Former Best Friend
-

 Entertainment2 weeks ago
Entertainment2 weeks agoCoronation Street Fans React as Todd Faces Heartbreaking Choice