Science
Researchers Capture First Images of Atomic Vibrations in 2D Materials
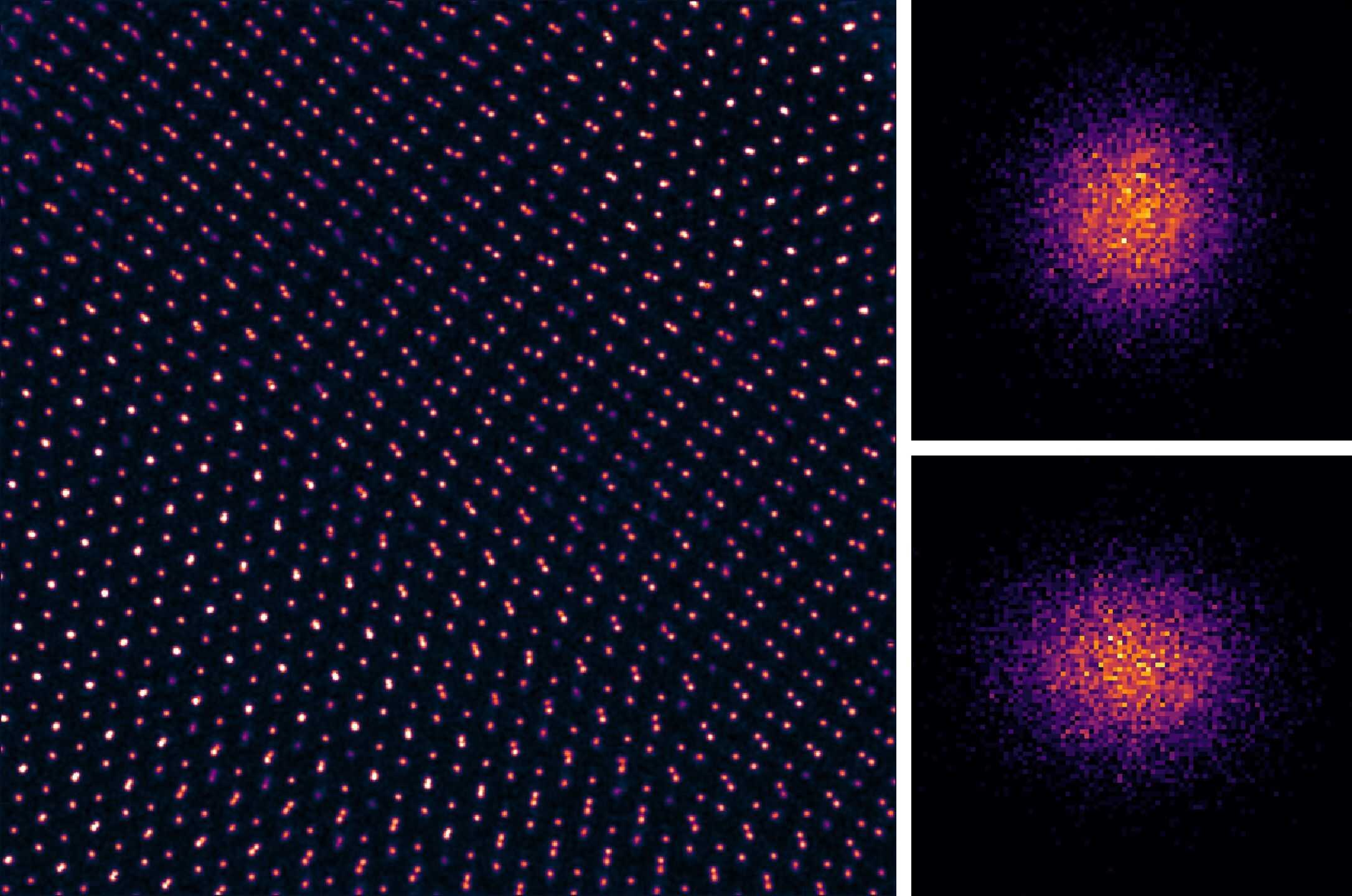
Researchers in the United States have made significant strides in the field of atomic physics by directly imaging a class of extremely low-energy atomic vibrations known as moiré phasons. This groundbreaking discovery confirms that these vibrations, previously considered theoretical, are indeed a primary mechanism through which atoms vibrate in specific twisted two-dimensional materials. The findings, published in the journal Science in August 2023, may have profound implications for understanding heat and charge transport, as well as quantum phase behaviors in these materials.
Yichao Zhang from the University of Maryland, who co-led the research with Pinshane Huang of the University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign, expressed enthusiasm about the work. “Phasons had only been predicted by theory until now, and no one had ever directly observed them, or even thought that this was possible,” Zhang stated. “Our work opens up an entirely new way of understanding lattice vibrations in 2D quantum materials.”
Understanding Moiré Patterns and Vibrational Modes
The research centers on the phenomenon that occurs when two sheets of two-dimensional materials are stacked and slightly twisted, creating a moiré pattern, or superlattice. This unique arrangement features quasi-periodic regions with rotationally aligned structures, referred to as AA or AB configurations, separated by networks of stacking faults called solitons. These materials exhibit distinctive vibrational modes known as moiré phonons, which can influence the physical properties of the materials based on the twist angle between layers.
In addition to moiré phonons, the presence of phasons in two-dimensional moiré materials had been theorized but never experimentally verified until this study. By employing a sophisticated microscopy technique called electron ptychography, the research team achieved an unprecedented spatial resolution of just 15 picometres (1 pm = 10^-12 m). This level of precision allowed them to detect subtle changes in thermally driven atomic vibrations by analyzing the shape and size of individual atoms.
Zhang detailed their findings: “What we found was striking: the vibrations weren’t uniform – atoms showed larger amplitudes in AA-stacked regions and highly anisotropic behaviour at soliton boundaries. These patterns align precisely with theoretical predictions for moiré phasons.”
Implications for Future Technologies
The implications of these findings extend beyond theoretical physics. Understanding phasons could pave the way for new materials with programmable thermal and electronic properties. Zhang emphasized that harnessing these vibrations could impact various fields, including low-power electronics, quantum computing, and nanoscale sensors.
The research team is now focused on further exploring how defects, strain, and interfaces affect phason behavior in real-world materials. Zhang highlighted the challenges posed by the low energy and spatial non-uniformity of phasons, which have made them difficult to detect using conventional experimental techniques. “To overcome this, we had to push electron ptychography to its limits and validate our observations through careful modeling and simulations,” she explained.
The ongoing investigations aim to reveal how phasons respond to external stimuli, such as temperature changes or applied fields. This could enhance understanding of their interactions with electrons, excitons, or other collective excitations in quantum materials.
As researchers continue to explore the intricate dynamics of moiré materials, this work stands as a pivotal step in revealing the complexities of atomic vibrations and their potential applications in next-generation technologies.
-

 Entertainment2 months ago
Entertainment2 months agoAnn Ming Reflects on ITV’s ‘I Fought the Law’ Drama
-

 Entertainment3 months ago
Entertainment3 months agoKate Garraway Sells £2 Million Home Amid Financial Struggles
-

 Health2 months ago
Health2 months agoKatie Price Faces New Health Concerns After Cancer Symptoms Resurface
-

 Entertainment2 months ago
Entertainment2 months agoCoronation Street’s Carl Webster Faces Trouble with New Affairs
-

 Entertainment2 months ago
Entertainment2 months agoWhere is Tinder Swindler Simon Leviev? Latest Updates Revealed
-

 Entertainment3 months ago
Entertainment3 months agoKim Cattrall Posts Cryptic Message After HBO’s Sequel Cancellation
-

 Entertainment2 months ago
Entertainment2 months agoOlivia Attwood Opens Up About Fallout with Former Best Friend
-

 Entertainment2 months ago
Entertainment2 months agoMasterChef Faces Turmoil as Tom Kerridge Withdraws from Hosting Role
-

 Entertainment3 months ago
Entertainment3 months agoMarkiplier Addresses AI Controversy During Livestream Response
-

 Entertainment4 months ago
Entertainment4 months agoSpeculation Surrounds Home and Away as Cast Departures Mount
-

 World2 months ago
World2 months agoCole Palmer’s Mysterious Message to Kobbie Mainoo Sparks Speculation
-

 Entertainment2 months ago
Entertainment2 months agoITV’s I Fought the Law: Unraveling the True Story Behind the Drama




















