Science
Scientists Decode Blood’s Molecular Messengers for First Time

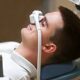
Research conducted at the Baker Heart and Diabetes Institute in Australia has made a groundbreaking discovery in understanding how the body communicates at a molecular level. For the first time, scientists have decoded the intricate messages carried by blood, unveiling the crucial role these molecular messengers play in cellular communication. This significant advancement offers new insights into health and disease management.
Every second, trillions of tiny parcels, known as exosomes, circulate through the bloodstream. These exosomes are more than just cellular byproducts; they contain vital information that can influence the behavior of other cells. The research team utilized advanced imaging techniques and sophisticated analytical methods to capture and interpret the content of these molecular messages.
Unveiling the Molecular Landscape
The study not only highlights the presence of these exosomes but also provides detailed information about their contents. Scientists discovered that these tiny structures carry proteins, lipids, and nucleic acids, which can significantly affect various physiological processes. The research emphasizes the potential of exosomes as biomarkers for diseases, including cardiovascular conditions and diabetes.
According to the lead researcher, Dr. David E. McLennan, understanding the role of these molecular messengers is crucial for developing innovative therapeutic strategies. “This breakthrough allows us to investigate how cells communicate and respond to their environment, which is fundamental for both health and disease,” he stated.
The implications of this research extend beyond basic science. By decoding the complex information within blood, scientists can explore new avenues for early detection and treatment of diseases. This could lead to more personalized medical approaches, improving patient outcomes and enhancing the overall understanding of human health.
Future Directions and Impact
As the research progresses, the team plans to delve deeper into how these molecular messengers interact with each other and their target cells. The findings may pave the way for developing novel diagnostic tools and therapeutic interventions that leverage the power of exosomes.
The study is part of a broader initiative at the Baker Heart and Diabetes Institute, which aims to advance cardiovascular and diabetes research. With funding from various health organizations, the research is poised to contribute significantly to global efforts in tackling these pressing health issues.
In conclusion, the decoding of blood’s molecular messengers marks a pivotal moment in medical research. The findings not only deepen our understanding of cellular communication but also hold promise for innovative solutions in disease management. As scientists continue to explore this fascinating area, the potential for improved health outcomes becomes increasingly tangible.
-

 Entertainment3 months ago
Entertainment3 months agoAnn Ming Reflects on ITV’s ‘I Fought the Law’ Drama
-

 Entertainment4 months ago
Entertainment4 months agoKate Garraway Sells £2 Million Home Amid Financial Struggles
-

 Health3 months ago
Health3 months agoKatie Price Faces New Health Concerns After Cancer Symptoms Resurface
-

 Entertainment3 months ago
Entertainment3 months agoCoronation Street’s Carl Webster Faces Trouble with New Affairs
-

 Entertainment3 months ago
Entertainment3 months agoWhere is Tinder Swindler Simon Leviev? Latest Updates Revealed
-

 World2 weeks ago
World2 weeks agoBailey Announces Heartbreaking Split from Rebecca After Reunion
-

 Entertainment4 months ago
Entertainment4 months agoMarkiplier Addresses AI Controversy During Livestream Response
-

 Entertainment2 weeks ago
Entertainment2 weeks agoCoronation Street Fans React as Todd Faces Heartbreaking Choice
-

 Science1 month ago
Science1 month agoBrian Cox Addresses Claims of Alien Probe in 3I/ATLAS Discovery
-

 Health4 months ago
Health4 months agoCarol Vorderman Reflects on Health Scare and Family Support
-

 Entertainment4 months ago
Entertainment4 months agoKim Cattrall Posts Cryptic Message After HBO’s Sequel Cancellation
-

 Entertainment3 months ago
Entertainment3 months agoOlivia Attwood Opens Up About Fallout with Former Best Friend